Authors: S.Ashok, Ambarish Narendran
In this work, a half-wave rectified sinusoidal waveform with a frequency of 50 Hz is analyzed in the time domain. The circuit in question carries out half-wave rectification, which transmits just the sinusoidal input’s positive half-cycles. By computing the integral of a half-wave rectified sinusoidal function modulated by an exponential decay factor, we are able to determine the response of the system. The final equation shows applications in rectified power supply circuits and provides insights into the decay dynamics of such a system.
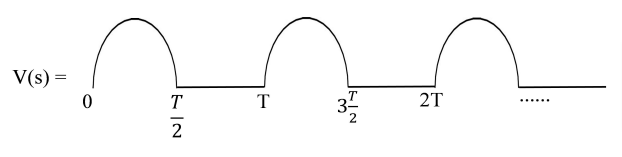
One of the simplest methods for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) is half-wave rectification. The negative half of an input AC waveform is blocked or eliminated during this procedure, leaving just the positive half through. Circuits for signal conditioning and power electronics often use this type of rectification.
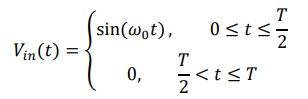
where ω0 = 2π×50 rad/s is the angular frequency corresponding to 50 Hz, and T is the period of the waveform.
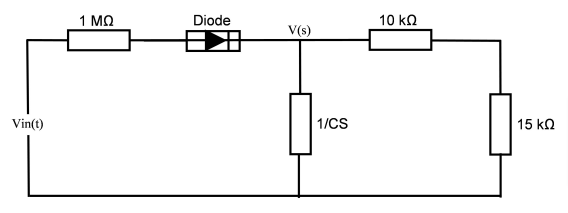
Additionally, the rectifier’s output voltage experiences exponential decay, a frequent feature in circuits containing resistive or inductive elements.
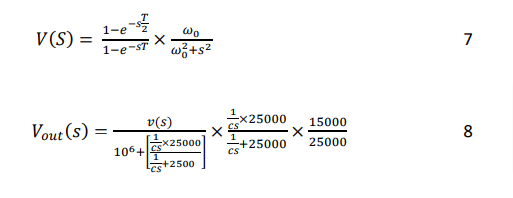
The output of the system can be represented as:
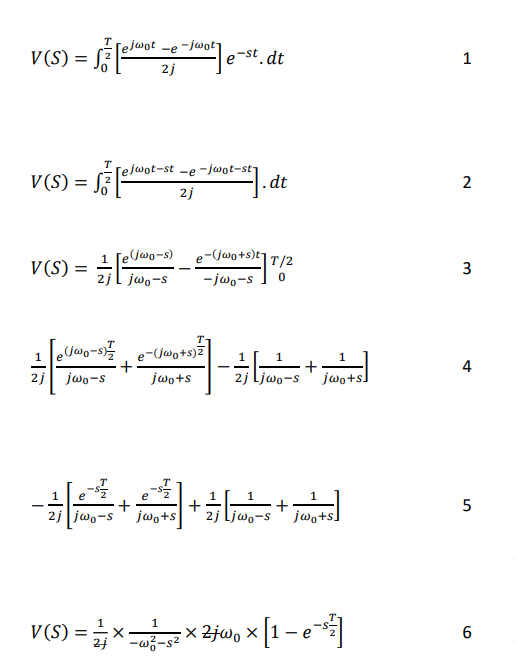
We obtained an analytical equation that includes exponential decay for the output voltage of a half-wave rectifier with an input frequency of 50 Hz. Final expression: